Generating custom Anaconda installers¶
As an Anaconda Enterprise Administrator, you can create custom environments. These environments include specific packages and their dependencies. You can then create a custom installer for the environment, that can be shipped to HDFS and used in Spark jobs.
Custom installers enable IT and Hadoop administrators to maintain close control of a Hadoop cluster while also making these tools available to data scientists who need Python and R libraries. They provide an easy way to ship multiple custom Anaconda distributions to multiple Hadoop clusters.
Creating an environment¶
Log in to the console using the Administrator credentials configured after installation.
Select Environments in the left menu.
Click Create in the upper right corner, give the environment a unique name and click Save.
Note
Environment names can contain alphanumeric characters and underscores only.
Check the channel you want to choose packages from, then select the specific packages–and version of each–you want to include in the installer.
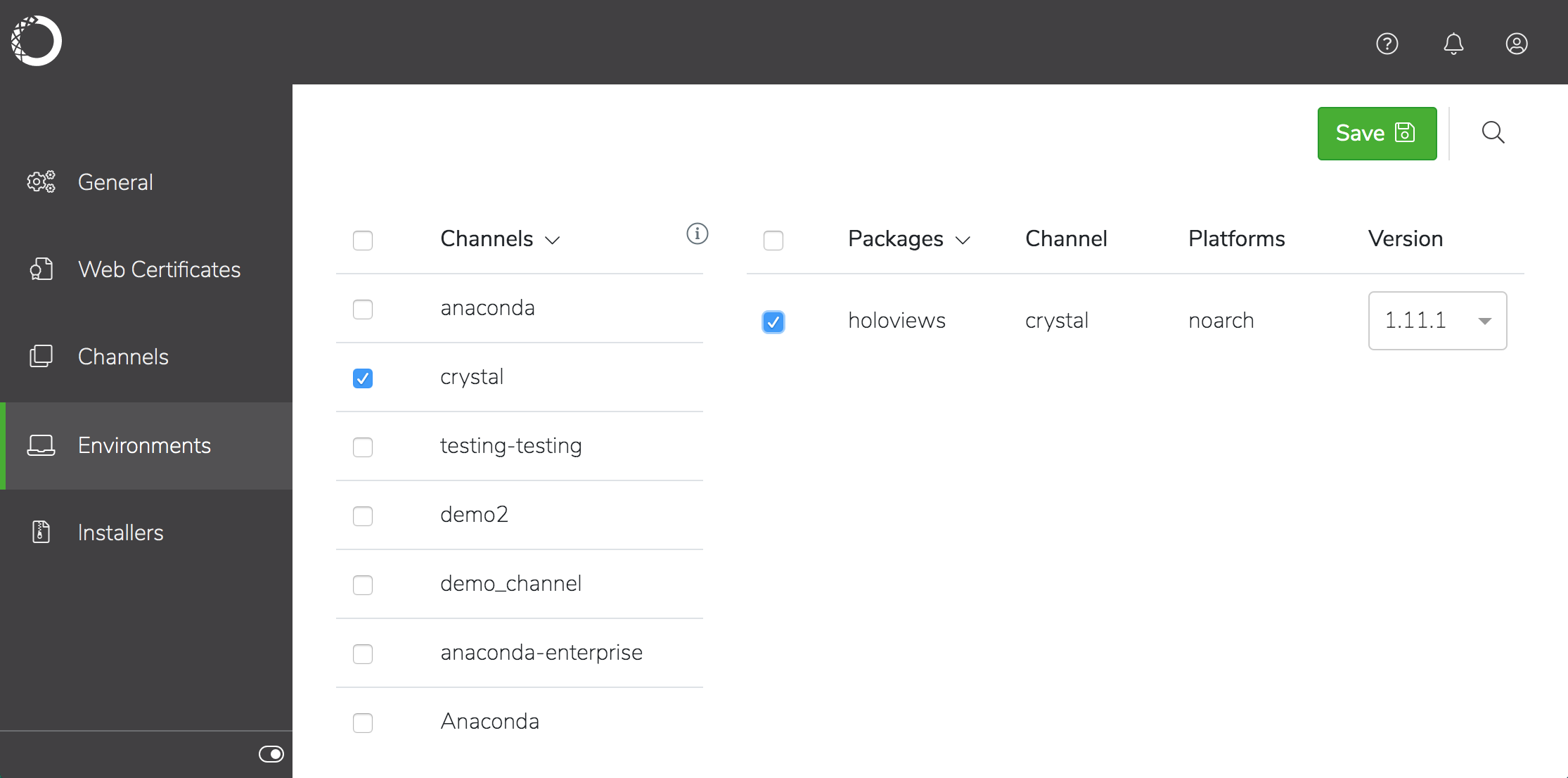
Click Save in the window banner to create the environment.
Anaconda Enterprise resolves all the package dependencies and displays the environment in the list. If there is an issue resolving the dependencies, you’ll be notified and prompted to edit the environment.
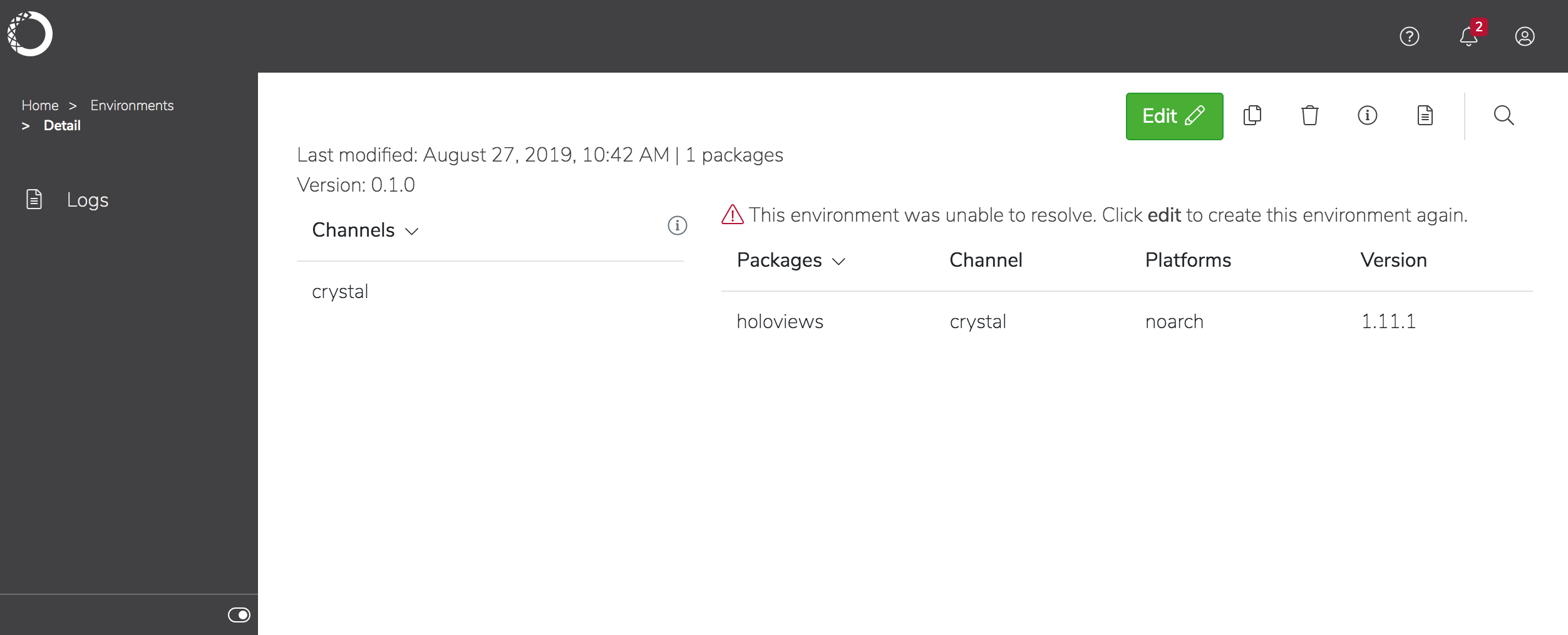
You can now use the environment as a basis for creating additional versions of the environment or other environments.
To edit an existing environment:
Click on an environment name to view details about the packages included in the environment, then click Edit.
Change the channels and/or packages included in the environment, and enter a version number for the updated package before clicking Save. The new version is displayed in the list of environments.
To copy an environment:
Enter a unique name for the environment and click Save. The new environment is diplayed in the list of environments.
Now that you’ve created an environment, you can create an installer for it.
Creating a custom installer for an environment¶
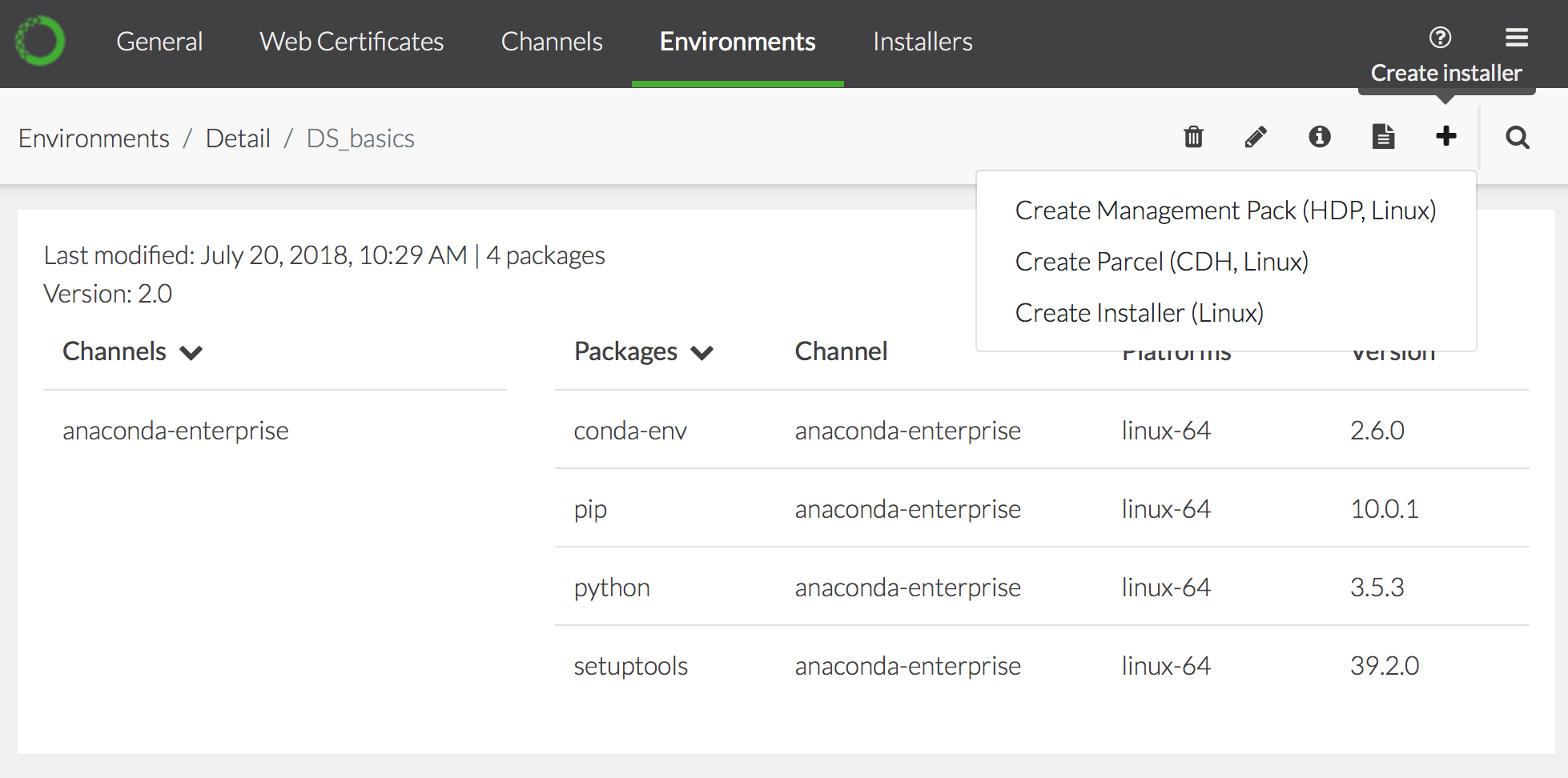
Select the environment in the list, click the Create installer icon
 , and select the type of installer you want to create:
, and select the type of installer you want to create:
Anaconda Enterprise creates the installer and displays it in the Installers list:
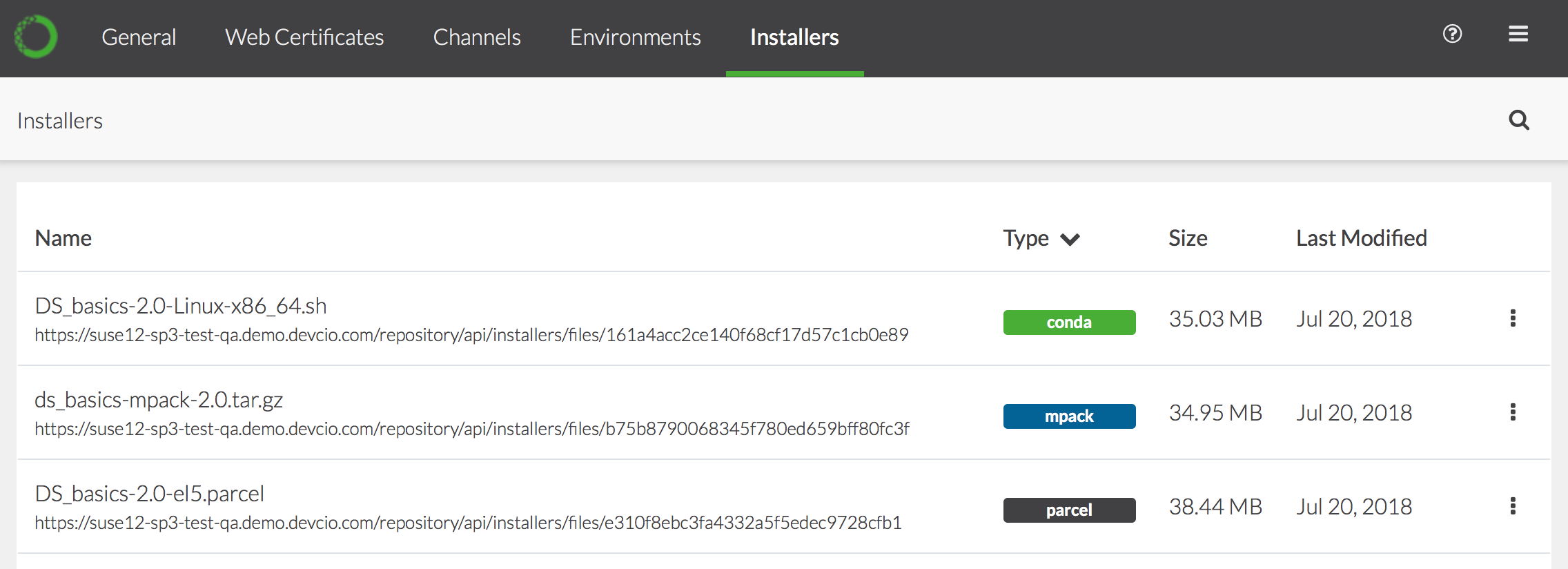
To view the relevant logs, download or delete the installer, click the
 icon and choose the appropriate command.
icon and choose the appropriate command.
If you created a management pack, you’ll need to install it on your Hortonworks HDP cluster and add it to your local Ambari server to make it available to users. For more information, see this blog post about generating custom management packs.
If you created a parcel, you’ll need to install it on your Cloudera CDH cluster to make it available to users:
Note
If you are using CDH 5.x, you’ll need to manually download the parcel, move it to the Cloudera Manager node, then configure Cloudera Manager for a local parcel repository. This is because CDH 5.x does not work with TLS 1.2 that Anaconda Enterprise uses to serve the parcel, so you’ll see a protocol version error if you attempt to use AE as a remote parcel repository with CDH 5.x.
If you are using CDH 6.x with parcels, you can configure Anaconda Enterprise as a remote parcel repository, or you can manually download the parcel and configure a local parcel repository.
In the Installers list, click the parcel name to view it’s details—including the logs generated during the creation process.
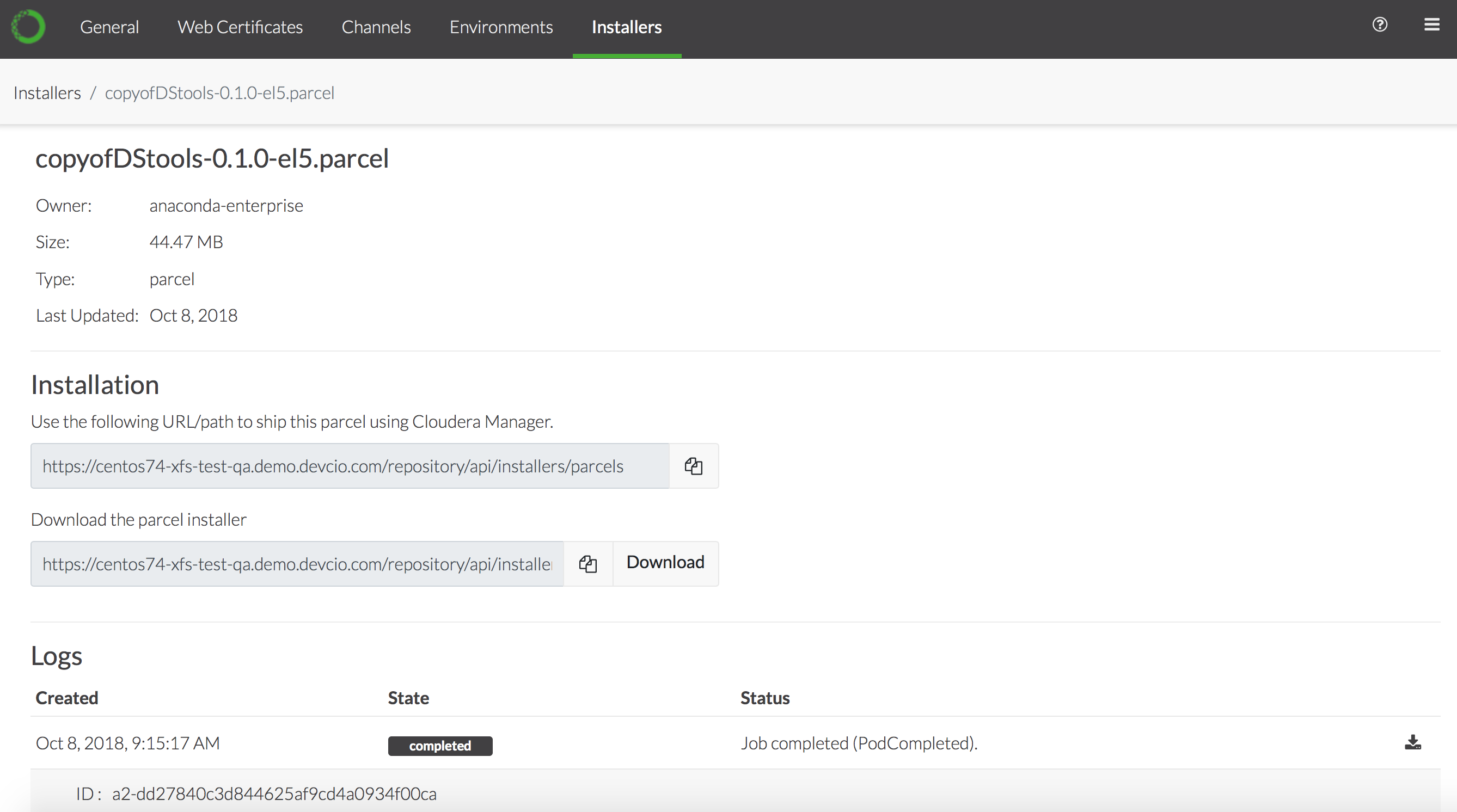
Depending on the version of CDH you are using (see NOTE above), either copy the path to the parcel or download the parcel installer.
From the Cloudera Manager Admin Console, click the Parcels indicator in the top navigation bar.
Click the Configuration button on the top right of the Parcels page to display the Parcel Settings.
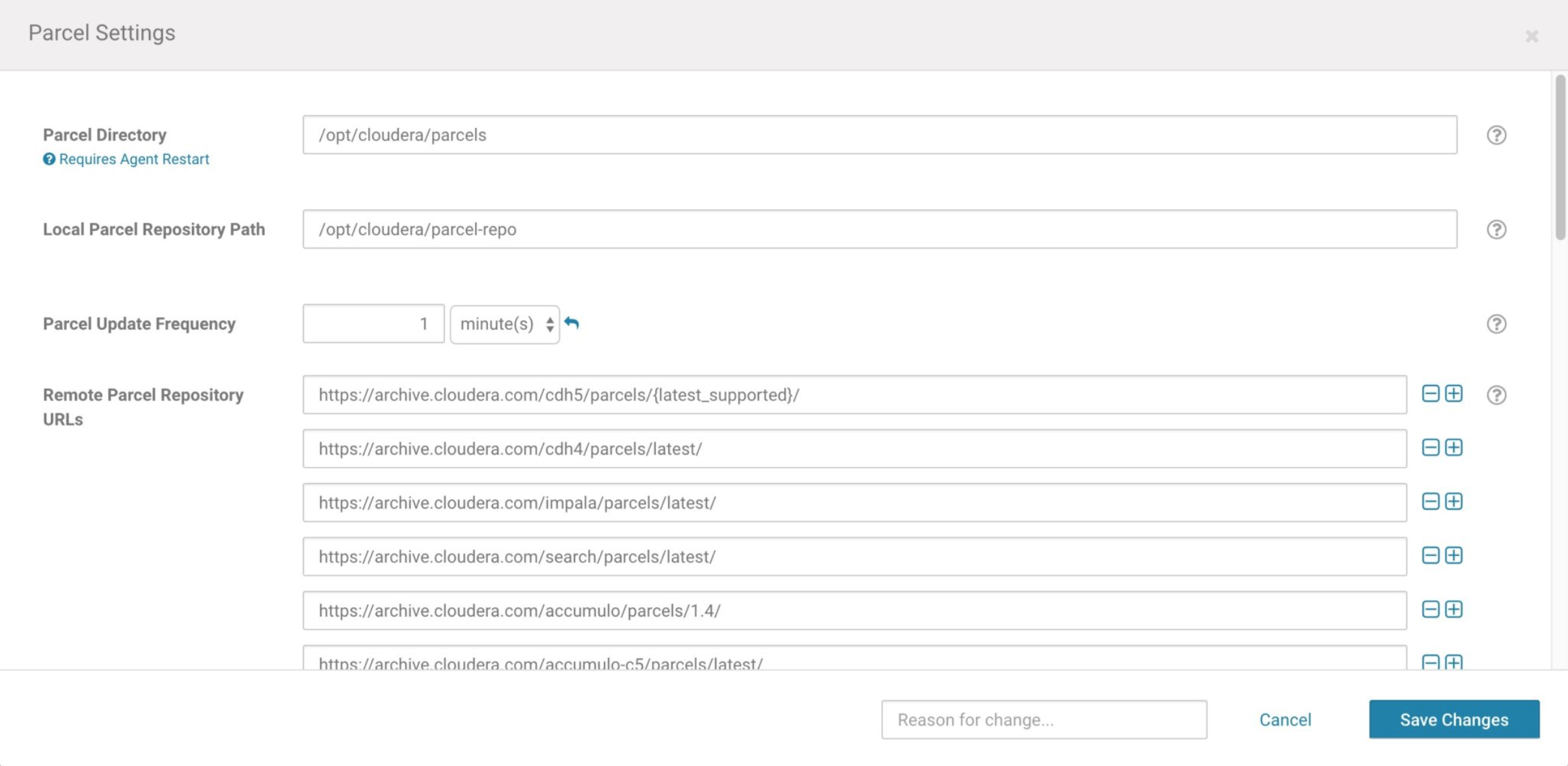
If you downloaded the parcel from AE in Step 2 above, copy it to the Local Parcel Repository Path you’ve configured for Cloudera Manager.
–or–
To configure AE as a remote parcel repository, add the URL you copied in Step 2 above to the Remote Parcel Repository URLs section and click Save Changes.
If automatic downloading and distribution are not enabled, go to the Parcels page and select Distribute to install the parcel across your CDH cluster. The custom-generated Anaconda parcel is now ready to use with Spark or other distributed frameworks on your Cloudera CDH cluster.
For more information, see these instructions from Cloudera.

