Connecting to an external version control repository¶
Anaconda Enterprise supports the use of an external version control repository for user-created projects. Anaconda recommends connecting to this external version control repository at time of installation, however you are also able to migrate from one version control repository to another after installation is complete.
To provide permission granularity and maintain parity with your external version control repository, Anaconda Enterprise will grant individual platform users access to individual repositories. To prevent default permissions being applied to all users within a group, users cannot belong to the given organization or group.
Platform users will be prompted for their access token before they create their first project in Anaconda Enterprise. Anaconda recommends you advise users to create an ever-lasting token, to retain permanent access to their files from within Anaconda Enterprise. The specific auth token permissions required for each repository are outlined here.
Make sure you have the following prerequisites before you begin:
The fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of your version control server.
The organization, team, or group name associated with your service account.
The username of the Administrator for the organization, team, or group. This user will require full Admin permissions.
The personal access token or password required to connect to your version control repository.
Supported external git versions
Anaconda Enterprise supports integration with the following external repositories:
External repository |
Supported versions |
|---|---|
GitHub Server |
2.15, through 3.4.1 |
GitHub Cloud |
github.com |
Bitbucket Server/DC |
5.9.1 through 7.21.0 |
Bitbucket Cloud |
bitbucket.org |
GitLab Self-Managed |
10.4.2 through 14.9.2 |
GitLab Cloud |
gitlab.com |
GitHub Enterprise Edition (Server)
Create a backup of the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap.Open the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap for editing.Locate the
gitsection (pictured below)
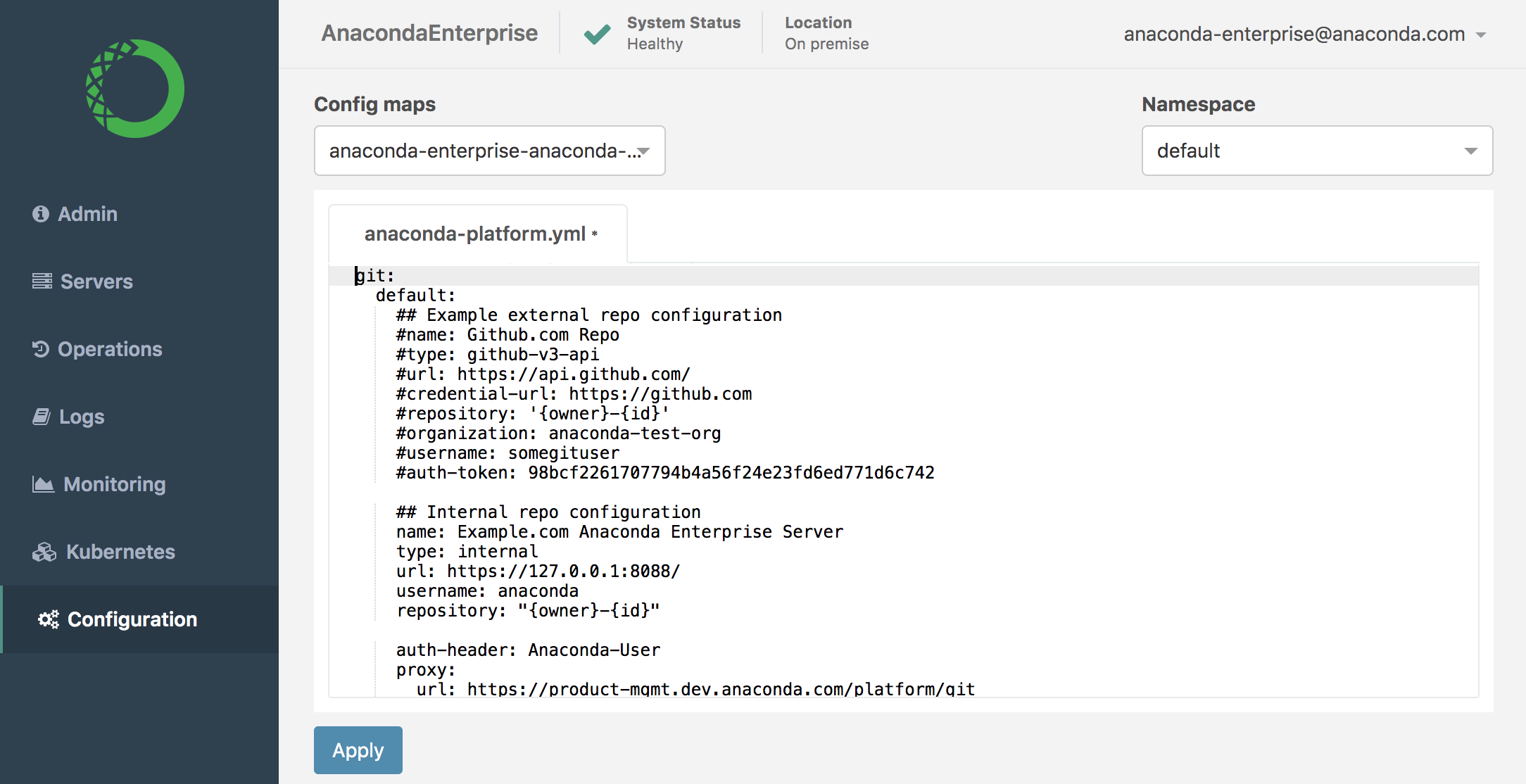
Uncomment the
Example external repo configurationsection.Comment the
Internal repo configurationsection.Configure the
Example external repo configuration.
name = A descriptive name for the service your organization uses.
type = The type of version control repository your organization uses: github-v3-api.
url = The URL of the API https://<FQDN>.com/api/v3/.
credential-url = The URL to authenticate against for repository operations such as cloning and pushing https://<FQDN>.com/api/v3/.
repository = Must be '{owner}-{id}' encased in single quotes.
organization = The name of your GitHub organization.
username = The username associated with the Administrator account. This account must have full Admin permissions.
auth-token = The personal access token for the Administrator account associated with the username.
Caution
The url and credential-url attributes must contain all lowercase characters.
EXAMPLE:
Save your changes.
Restart system pods with the following command for changes to take effect:
Once all pods have returned to a running state, users should now be prompted to add their personal access token after logging into the platform.
GitHub Enterprise Edition (Cloud)
Create a backup of the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap.Open the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap for editing.Locate the
gitsection (pictured below)

Uncomment the
Example external repo configurationsection.Comment the
Internal repo configurationsection.Configure the
Example external repo configuration.
name = A descriptive name for the service your organization uses.
type = The type of version control repository your organization uses: github-v3-api.
url = The URL of the API https://api.github.com/.
credential-url = The URL to authenticate against for repository operations such as cloning and pushing https://github.com/<github-organization>.
repository = Must be '{owner}-{id}' encased in single quotes.
organization = The name of your GitHub organization.
username = The username associated with the Administrator account. This account must have full Admin permissions.
auth-token = The personal access token for the Administrator account associated with the username.
Caution
The url and credential-url attributes must contain all lowercase characters.
EXAMPLE:
Save your changes.
Restart system pods with the following command for changes to take effect:
Once all pods have returned to a running state, users should now be prompted to add their personal access token after logging into the platform.
Bitbucket Server/Data Center
Create a backup of the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap.Open the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap for editing.Locate the
gitsection (pictured below)

Uncomment the
Example external repo configurationsection.Comment the
Internal repo configurationsection.Configure the
Example external repo configuration.
name = A descriptive name for the service your organization uses.
type = The type of version control repository your organization uses: bitbucket-v1-api.
url = The URL of the API https://<FQDN>:7990.
credential-url = The URL to authenticate against for repository operations such as cloning and pushing https://<FQDN>:7990.
repository = Must be '{owner}-{id}' encased in single quotes.
organization = The name of your Bitbucket team.
username = The username associated with the Administrator account. This account must have full Admin permissions.
auth-token = The Bitbucket app password for the Administrator account associated with the username.
Caution
The url and credential-url attributes must contain all lowercase characters.
EXAMPLE:
Save your changes.
Restart system pods with the following command for changes to take effect:
Once all pods have returned to a running state, users should now be prompted to add their app password after logging into the platform.
Bitbucket Cloud
Note
Bitbucket.com does not support versioning of archive downloads and app deployments. In other words, the latest revision will always be downloaded or deployed.
Create a backup of the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap.Open the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap for editing.Locate the
gitsection (pictured below)

Uncomment the
Example external repo configurationsection.Comment the
Internal repo configurationsection.Configure the
Example external repo configuration.
name = A descriptive name for the service your organization uses.
type = The type of version control repository your organization uses: bitbucket-v2-api.
url = The URL of the API https://api.bitbucket.org.
credential-url = The URL to authenticate against for repository operations such as cloning and pushing https://bitbucket.org.
repository = Must be '{owner}-{id}' encased in single quotes.
organization = The name of your Bitbucket team.
username = The username associated with the Administrator account. This account must have full Admin permissions.
auth-token = The Bitbucket app password for the Administrator account associated with the username.
Caution
The url and credential-url attributes must contain all lowercase characters.
EXAMPLE:
Save your changes.
Restart system pods with the following command for changes to take effect:
Once all pods have returned to a running state, users should now be prompted to add their app password after logging into the platform.
Gitlab Enterprise Edition (Self-Managed)
Create a backup of the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap.Open the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap for editing.Locate the
gitsection (pictured below)

Uncomment the
Example external repo configurationsection.Comment the
Internal repo configurationsection.Configure the
Example external repo configuration.
name = A descriptive name for the service your organization uses.
type = The type of version control repository your organization uses: gitlab-v4-api.
url = The URL of the API https://<FQDN>.com.
credential-url = The URL to authenticate against for repository operations such as cloning and pushing https://<FQDN>.com.
repository = Must be '{owner}-{id}' encased in single quotes.
organization = The name of your GitLab group.
username = The username associated with the Administrator account. This account must have full Admin permissions.
auth-token = The access token for the Administrator account associated with the username.
Caution
The url and credential-url attributes must contain all lowercase characters.
EXAMPLE:
Save your changes.
Restart system pods with the following command for changes to take effect:
Once all pods have returned to a running state, users should now be prompted to add their access token after logging into the platform.
Gitlab Enterprise Edition (Cloud)
Note
GitLab.com does not support versioning of archive downloads and app deployments. In other words, the latest revision will always be downloaded or deployed.
Create a backup of the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap.Open the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap for editing.Locate the
gitsection (pictured below)

Uncomment the
Example external repo configurationsection.Comment the
Internal repo configurationsection.Configure the
Example external repo configuration.
name = A descriptive name for the service your organization uses.
type = The type of version control repository your organization uses: gitlab-v4-api.
url = The URL of the API https://gitlab.com.
credential-url = The URL to authenticate against for repository operations such as cloning and pushing https://gitlab.com.
repository = Must be '{owner}-{id}' encased in single quotes.
organization = The name of your GitLab group.
username = The username associated with the Administrator account. This account must have full Admin permissions.
auth-token = The access token for the Administrator account associated with the username.
Caution
The url and credential-url attributes must contain all lowercase characters.
EXAMPLE:
Save your changes.
Restart system pods with the following command for changes to take effect:
Once all pods have returned to a running state, users should now be prompted to add their access token after logging into the platform.
