Specifying alternate wildcard domains#
By default, Anaconda Enterprise expects the wildcard domain to be the same for the primary platform server and the application domain.
If your particular implementation uses different domains, you’ll need to update the configuration file for the platform with the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for each server.
Note
Make sure the wildcard domain has a TLS cert and DNS entry that meets these requirements before you follow the process below to specify it as an apps-host or workspace-host.
Log in to Anaconda Enterprise, select the Menu icon
 in the top right corner and click the Administrative Console link displayed at the bottom of the slide out window.
in the top right corner and click the Administrative Console link displayed at the bottom of the slide out window.Click Manage Resources.
Log in to the Operations Center using the Administrator credentials configured after installation.
Select Configuration from the menu on the left.
Verify that the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlconfiguration file is selected in the Config map drop-down menu.Note
Any changes you make will impact how Anaconda Enterprise functions, so we strongly recommend that you save a copy of the original file before making any changes.
Scroll down to the
Deployment server configurationsection of the Config map: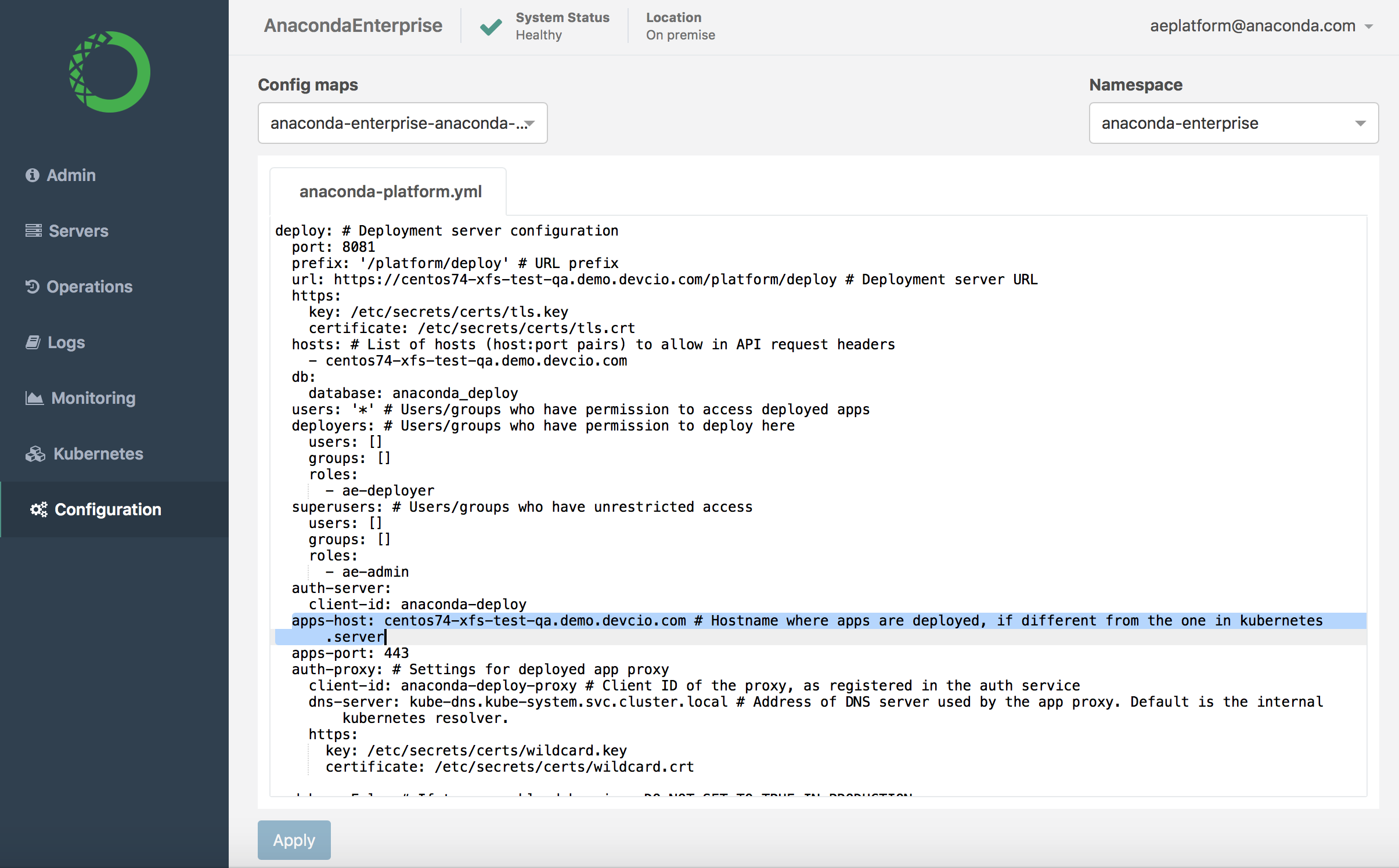
Search for and update the
apps-hostsetting with the FQDN of the host server you’ll be deploying apps to, if it’s different than the default Kubernetes server.Scroll down to the
Workspace server configurationsection of the Config map: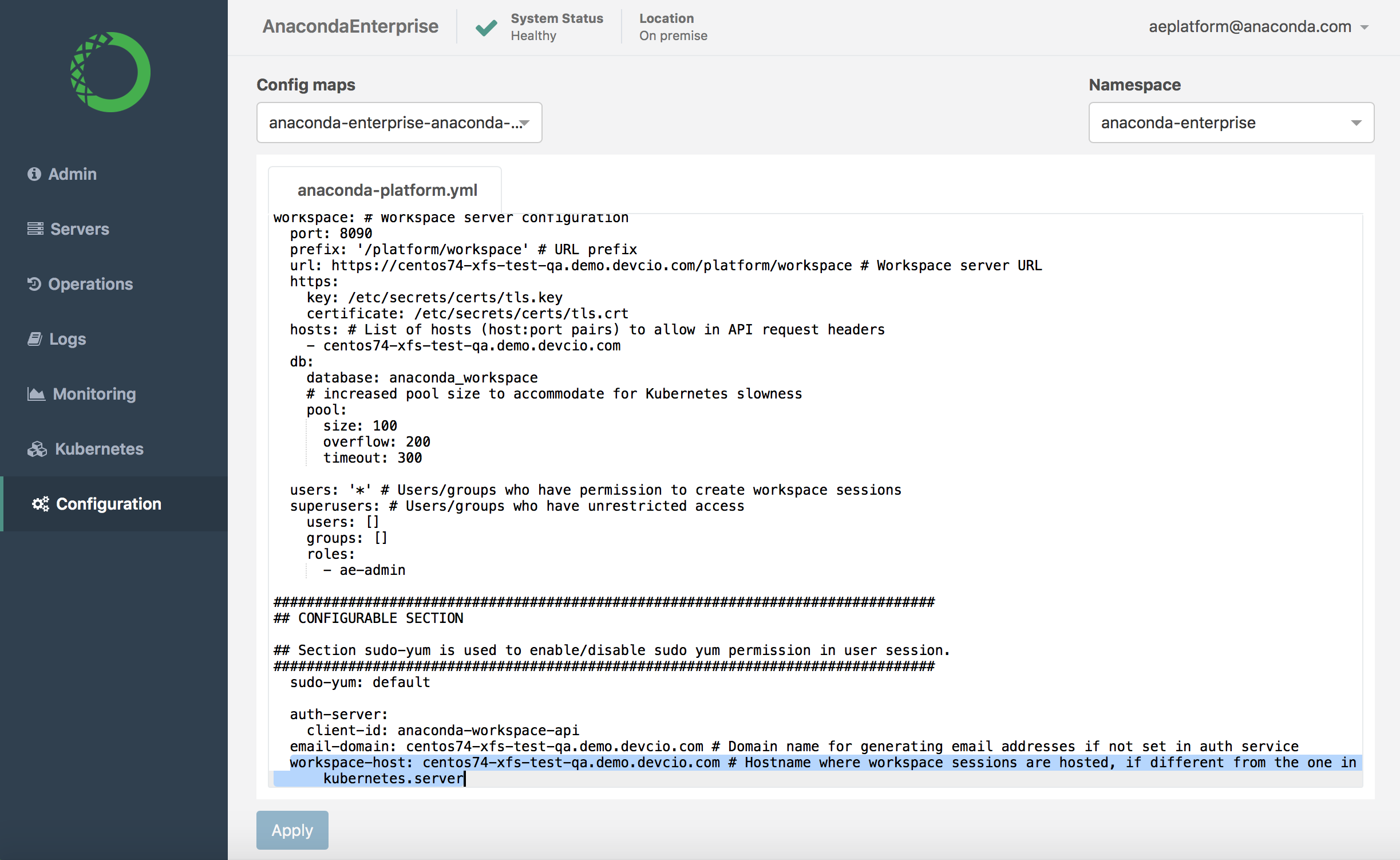
Update the
workspace-hostsetting with the FQDN of the host server you’ll be using as a workspace server, if it’s different than the default Kubernetes server.Click Apply to save your changes.
To update the Anaconda Enterprise server with your changes, restart services by running these commands on the master node:
sudo gravity enter kubectl get pods | grep ap- | cut -d' ' -f1 | xargs kubectl delete pods