Upgrading Anaconda Enterprise 5 on Gravity#
Contact the Anaconda implementation team before you begin for assistance upgrading your version of Anaconda Enterprise 5. Follow along with these instructions as an Anaconda implementation team member guides you through the upgrade process.
Prerequisites#
You must have
jqinstalled.You must have a service account with
sudoaccess on your Kubernetes (K8s) master node.Your K8s master node must be configured with a DNS A record. The A record sets the domain name you use for your Anaconda Enterprise instance.
If you are upgrading Anaconda Enterprise on a system with multiple nodes, you must verify the clock on each node is in sync with the others. Anaconda recommends using Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize computer system clocks automatically over your network. For more information on installing and using
Chronyto manage the NTP, see the instructions provided here.You must have the
ae-preflightpackage installed. For more information, see Anaconda Enterprise pre-flight check.Create a backup of your
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlConfigMap by running the following command:kubectl get cm anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.yml -o json | jq -r '.data["anaconda-platform.yml"]' > configmap-backup.yml
Caution
Anaconda recommends the use of managed persistence to ensure open sessions and deployments are captured by the upgrade process. If you are not using managed persistence, have all users save their work, stop any open sessions and deployments, and log out of the platform during the upgrade process.
Upgrading#
After you have verified that your system meets all of the installation requirements, you’re ready to upgrade the cluster.
There are two basic types of upgrades for Gravity users: in-place upgrades and fresh reinstallation upgrades. Follow along with the instructions here as your Anaconda implementation team member guides you through upgrading your software.
Caution
Project sessions are terminated during the upgrade process! Because of this, it is important to stop all sessions prior to upgrading. If you do not, sessions that are terminated as part of the upgrade process must be restarted manually post upgrade.
Sessions can be stopped programmatically using
ae5-toolsby running the following command in a terminal that has access your Workbench cluster over the network:ae5 session list --columns=id --no-header | xargs -n1 ae5 session stop --yes
In-place upgrade#
Warning
In-place upgrades of Anaconda Enterprise are not supported for versions that are moving from Gravity 6 to Gravity 7. Instead, you must perform a fresh reinstallation to upgrade your software. If you do not, your installation will break. Check the version of Gravity and Enterprise before you begin, and choose the upgrade process that best suits your needs.
In-place upgrades are also not supported when upgrading from Anaconda Enterprise 5.6.x to 5.6.2. Please perform a fresh reinstallation to upgrade between these versions.
In-place upgrades are performed while the software is still running. To perform an in-place upgrade:
Log in to a service account with
sudoaccess on the master node running your Anaconda Enterprise software.Download the installer file by running the following command:
# Replace <INSTALLER_LOCATION> with the provided location of the installer file curl -O <INSTALLER_LOCATION>
Decompress the installer file by running the following command:
# Replace <INSTALLER> with the installer file you just downloaded tar xvzf <INSTALLER>
Enter the installer directory by running the following command:
# Replace <INSTALLER> with the version of your installer cd <INSTALLER>
Run the following command to verify your environment is properly prepared:
ae-preflight
If the check returns an overall result of WARN, you can view the results of the check by running the following command:
cat results.txt
If necessary, make applicable corrections to properly prepare your environment to meet the Installation requirements. Once you’ve verified that your environment is properly configured, you can begin the upgrade process.
To start the upload and upgrade process, run the following commands:
sudo ./upload sudo ./gravity upgrade
The upgrade process can take up to an hour or more to complete, primarily due to the upload step. You can view the status of the upgrade process at any time by running the following command:
sudo watch ./gravity plan
Once the upgrade process is complete, the pods will start to come up on their own, but this process also takes some time to finish. Monitor the pods status by running the following command:
sudo watch kubectl get pods
If you encounter errors while doing your in-place upgrade, you can view which phase of the upgrade failed by running the following command:
sudo ./gravity plan
You can return to any phase of the upgrade process by running the rollback command against the name of the phase as it’s listed in the Phase column of the
./gravity plancommands’ return:# Replace <NAME_OF_PHASE> with the name listed in the Phase column sudo ./gravity plan rollback --phase=/<NAME_OF_PHASE>
After addressing any errors, resume the upgrade by running the following command:
sudo ./gravity upgrade --resume --force
Once you have resolved your errors, or if no errors have occurred, it’s time to verify your installation.
Fresh reinstallation upgrade#
A fresh reinstallation upgrade backs up your current Anaconda Enterprise software configurations and settings, then uninstalls and reinstalls the software. After installation is complete, you can apply your saved configurations and settings to the new software version.
To perform a fresh reinstallation upgrade:
Back up your configurations
Log in to a service account with
sudoaccess on the master node running your Anaconda Enterprise software.Download the installer file by running the following command:
# Replace <INSTALLER_LOCATION> with the provided location of the installer file curl -O <INSTALLER_LOCATION>
Decompress the installer file by running the following command:
# Replace <INSTALLER> with the installer file you just downloaded tar xvzf <INSTALLER>
Enter the installer directory by running the following command:
# Replace <INSTALLER> with the installer file you just decompressed cd <INSTALLER>
Note
The installer bundle contains the
extract_config.shscript, which retains the following files when run:anaconda-enterprise-certs.yamlanaconda-enterprise-keycloak.yamlhelm_values.yamlgravity_values.yaml
Create a directory to contain the configuration data extracted by the script and name it “reinstall”:
mkdir reinstall
Enter the directory you just created:
cd reinstall
Run the
extract_config.shscript by running the following command:sudo bash extract_config.sh
Once the script has completed, you will need to manually save some additional configurations and secrets to your
reinstalldirectory.Export your configmap to a
.yamlfile by running the following command:sudo kubectl get cm -o yaml --export > configmap.yaml
Uninstall
Uninstall Anaconda Enterprise on all nodes and reboot your instance.
Warning
Do not run the command sudo rm -rf /opt/anaconda/storage on the master node as part of your uninstall process. If you do you, will lose your configuration settings and user data.
Reinstall and apply your saved settings
Run the following command to verify your environment is properly prepared:
ae-preflight
If the check returns an overall result of WARN, you can view the results of the check by running the following command:
cat results.txt
If necessary, make applicable corrections to properly prepare your environment to meet the Installation requirements. Once you’ve verified that your environment is properly configured, you can begin the upgrade process.
Run the Gravity installation command using the
gravity_values.yamlfile stored in the reinstall directory you created earlier instead of creating a new file during installation:# Replace <ADVERTISE-ADDR> with the IP address you want to be visible to the other nodes. If you have a private network and all nodes can communicate on it, use the private IP address for the advertise address # Replace <CLUSTERNAME> with the name you're giving to your cluster. Alphanumeric characters and periods only # Replace <VALUES_PATH> with the filepath to the gravity_values.yaml file created from running the extract_config.sh script sudo ./gravity install --advertise-addr=<ADVERTISE-ADDR> --cluster=<CLUSTERNAME> --config <VALUES_PATH> --service-uid=$(id -u) --cloud-provider=generic
Here is an example of what the installation command looks like for a single-node cluster:
sudo ./gravity install --advertise-addr=192.168.1.1 --cluster=MyCluster --config ./gravity_values.yaml --service-uid=$(id -u) --cloud-provider=generic
Replace your SSL certificate by running the following commands:
sudo kubectl create -f anaconda-enterprise-certs.json sudo kubectl replace -n kube-system -f cluster-tls.json
Replace your user secrets by running the following command:
sudo kubectl create -f user-secrets.json
The
configmap.yamlfile that you created earlier contains settings that need to be restored to theanaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlfile manually.Open a web browser and log in to Anaconda Enterprise as an Administrator.
Open the User dropdown menu and select Admin Console.
Select Manage Resources to open your Gravity Ops Center.
Log in to your Gravity Ops Center. Contact your Gravity systems administrator if you need access.
Select Kubernetes from the left-hand navigation menu.
Select Edit config map under
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlto open the file. Leave this browser open for now.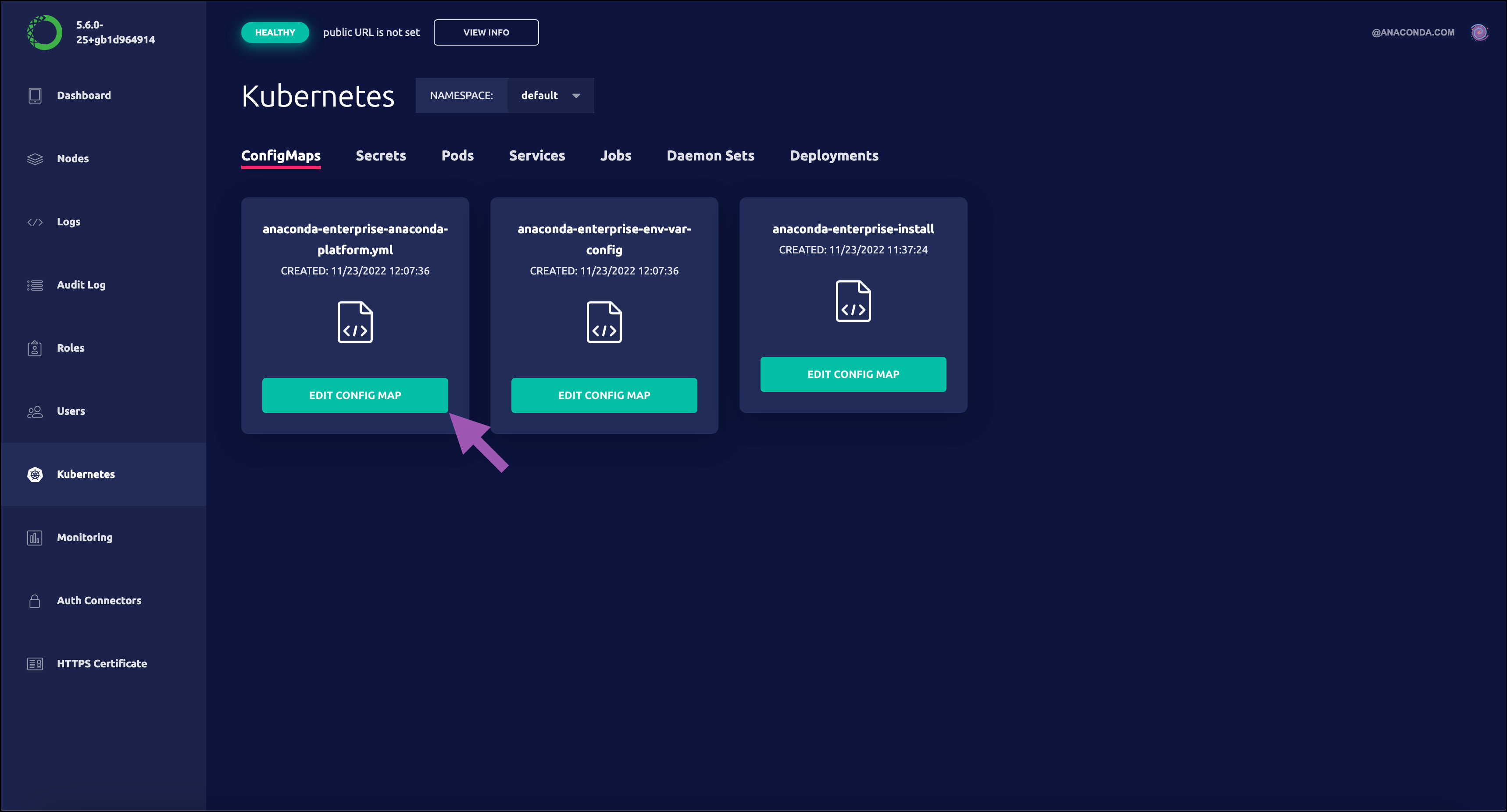
Return to your terminal and view the contents of your
configmap.yamlfile by running the following command:cat configmap.yaml
Review the contents of the
anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlfile and verify that your configuration values have been properly restored. If necessary, replace the applicable sections of theanaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlfile with the configurations saved in yourconfigmap.yamlfile.Restart the Anaconda platform pods by running the following command:
kubectl get pods | grep ap- | cut -d ' ' -f 1 | xargs kubectl delete pods
Once the upgrade process is complete, it’s time to verify your installation.
Verifying your installation#
Verify all pods are running by running the following command:
sudo kubectl get pods
Open a web browser and navigate to your Authentication Center.
# Replace <FQDN> with the fully qualified domain name of your Anaconda Enterprise server https://<FQDN>/auth/admin
Select Users from the Manage menu, then click View all users and verify your users’ data is present.
Open a web browser and navigate to your Anaconda Enterprise URL. Log in using the same credentials you used for your previous installation.
Review the Projects list to verify that all project data has been restored.
Additional configurations#
TLS/SSL certificates#
If you did not configure SSL certificates as part of the post-install configuration, do so now. For more information, see Updating TLS/SSL certificates.
External git repository#
Anaconda Enterprise 5 uses configurable parameters in the External git section of the anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.yml file to connect to external git repositories. Verify your parameters are mapped correctly, as described here.
Spark/Hadoop#
After verifying your installation, run the following command on the master node of the Anaconda Enterprise server:
# Replace <PATH_TO_SECRETS.yaml> with the path to your anaconda secrets .yaml file
sudo kubectl replace -f <PATH_TO_SECRETS.yaml>
To verify that your configuration upgraded correctly:
Log in to Anaconda Enterprise.
If your configuration uses Kerberos authentication, open a Hadoop terminal and authenticate yourself through Kerberos using the same credentials you used previously. For example,
kinit <USERNAME>.Open a Jupyter Notebook that uses Sparkmagic and verify that it behaves as expected by running the
sccommand to connect to Sparkmagic and start Spark.
Cleaning up#
As part of the upgrade process, the script you run automatically removes the unused packages and images from the previous installation and repopulates the registry to include only those images required by the current installation. This helps prevent the cluster from running out of disk space on the master node.