Migrating projects between version control repositories#
If your organization has changed Git hosting services, and you therefore need to migrate projects from one supported version control repository to another, Anaconda recommends you follow this high-level process:
Prerequisites:
Update the Data Science & AI Workbench config map with the information required to connect to the external version control repository.
To run the project migration script, you’ll need Administrator access to a command line tool that can run bash or Python scripts on the master node of the Workbench cluster.
Ensure a recent version of
gitis installed on the master nodeYou’ll also need the origin Git host token/password, and destination Git host token/password.
Pre-migration setup#
If you haven’t already done so, on the master node, change to the directory of the unpacked Workbench installer and install the bootstrap conda environment:
bash conda-bootstrap.sh
After the environment is finished installing, you may need to log out and log back in to activate the conda environment.
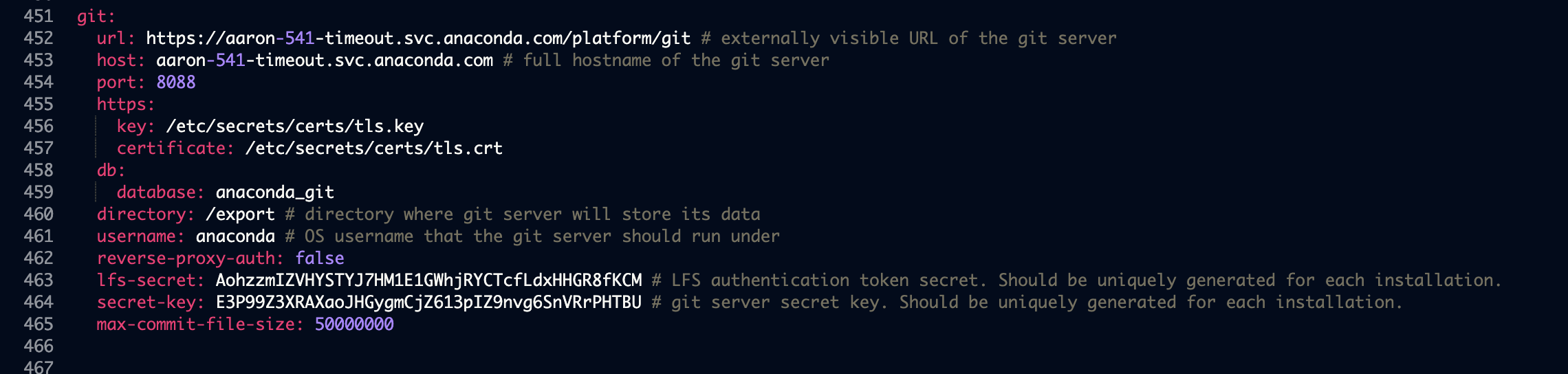
Temporarily disable reverse proxy authentication by adding the following key-value pair to the
gitsection (outside of thestoragesection in the config map) of theanaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.ymlfile used to configure the platform to use an external version control repository:reverse-proxy-auth: false
This should look similar to the following:
Run the following command to restart the associated pod on the master node:
kubectl delete pod -l 'app=ap-git-storage'
Create a user mappings file that maps Workbench user IDs to Git user IDs. This is a colon-separated text file where the first field is the Workbench user name, and the second field is the corresponding Git user name. For example:
ae-admin:git-admin ae-user1:git-user1 ae-user2:git-user2
Note
If you intend on migrating to or from a Bitbucket repository, you must use your
Bitbucket account IDinstead of yourBitbucket usernamein theuser mappings file.
Using the migration tool#
Caution
Using the migration tool with https instead of http for the
internal storage may result in an SSL error.
The migration tool is a Python script, migrate_projects.py, found in the Workbench
installation tarball. It can be used in the following ways:
usage: migrate_projects.py [-h] [--parallel PARALLEL] [--log-file LOG_FILE]
[--force-migrate] [--scratch-dir SCRATCH_DIR]
--postgres-host POSTGRES_HOST
[--postgres-user POSTGRES_USER]
[--postgres-passwd POSTGRES_PASSWD]
[--origin-api-type {internal,bitbucket-v1-api,bitbucket-v2-api,github-v3-api,gitlab-v4-api}]
--origin-api-url ORIGIN_API_URL
[--origin-username ORIGIN_USERNAME]
[--origin-token ORIGIN_TOKEN]
[--origin-organization ORIGIN_ORGANIZATION]
[--dest-api-type {internal,bitbucket-v1-api,bitbucket-v2-api,github-v3-api,gitlab-v4-api}]
--dest-api-url DEST_API_URL
[--dest-username DEST_USERNAME]
[--dest-token DEST_TOKEN]
[--dest-organization DEST_ORGANIZATION]
--dest-user-mappings DEST_USER_MAPPINGS
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--cloud Set if using Gitlab Cloud, or older version of Gitlab On-Prem
--parallel PARALLEL Number of parallel migration jobs to spawn
--log-file LOG_FILE Path prefix to log directory, suffixed with a
timestamp, e.g. migrate-projects-
log-1559234750640867208
--force-migrate Forces migration by replacing local and destination
repositories
--scratch-dir SCRATCH_DIR
The scratch directory for cloning project repositories
--postgres-host POSTGRES_HOST
Hostname of Workbench Postgres DB
--postgres-user POSTGRES_USER
Username of Workbench postgres DB
--postgres-passwd POSTGRES_PASSWD
Password of Workbench postgres DB
--origin-api-type {internal,bitbucket-v1-api,bitbucket-v2-api,github-v3-api,gitlab-v4-api}
Origin git host API type
--origin-api-url ORIGIN_API_URL
Origin git host API URL (must be all lowercase)
--origin-username ORIGIN_USERNAME
Origin git host username
--origin-token ORIGIN_TOKEN
Origin git host auth token
--origin-organization ORIGIN_ORGANIZATION
Origin git host organization
--dest-api-type {internal,bitbucket-v1-api,bitbucket-v2-api,github-v3-api,gitlab-v4-api}
Destination git host API type
--dest-api-url DEST_API_URL
Destination git host API URL (must be all lowercase)
--dest-username DEST_USERNAME
Destination git host username
--dest-token DEST_TOKEN
Destination git host auth token
--dest-organization DEST_ORGANIZATION
Destination git host organization
--dest-user-mappings DEST_USER_MAPPINGS
Colon-separated Workbench-to-git-host mappings file, e.g. ae-
user1:github-user1
For example, the tool can be used in the following way:
python migrate_projects.py \
--postgres-host localhost --origin-api-url http://localhost:8443/ \
--origin-username root --dest-api-type gitlab-v4-api \
--dest-api-url https://mbrock-gitlab.anacondaenterprise.com/ \
--dest-username root --dest-organization demo --dest-user-mappings \
user-mappings-gitea-to-gitlab.txt --force-migrate --parallel 4
To ensure tokens are not visible in bash history, they can be omitted and can be entered via stdin when running the script.
Note
The postgres password can be left blank. When migrating from Workbench, the origin-token can be left blank.
When migrating to Workbench, the dest-token can be left blank.
Note
When migrating to Gitlab Cloud, please use the --cloud flag.
Post-migration cleanup#
After the script finishes migrating the projects, re-enable reverse proxy
authentication by editing the key-value pair you previously added to the
git section of the anaconda-enterprise-anaconda-platform.yml file,
so it looks like the following:
reverse-proxy-auth: true
Caution
If you do not re-enable reverse proxy authentication, Workbench will not work.
To verify that the new repository is being used by Workbench, edit an existing project and commit your changes to it.
Adding collaborators#
If you’ve migrated to github, whenever a user is added to a project as a collaborator, they’ll be sent an invitation to collaborate via email. They’ll need to accept this invitation to be able to commit changes to the repository associated with the project. This does not apply to Github Enterprise.