Visualizations and dashboards#
Data Science & AI Workbench makes it easy for you to create and share interactive data visualizations, live notebooks or machine learning models built using popular libraries such as Bokeh and HoloViews.
To get you started quickly, Workbench provides sample projects of Bokeh applications for clustering and cross filtering data. There are also several examples of Workbench projects that use HoloViz here.
Follow these steps to create an interactive plot:
From the Projects view, select Create + > New Project and create a project from the
Anaconda 3.6 (v5.0.1)template: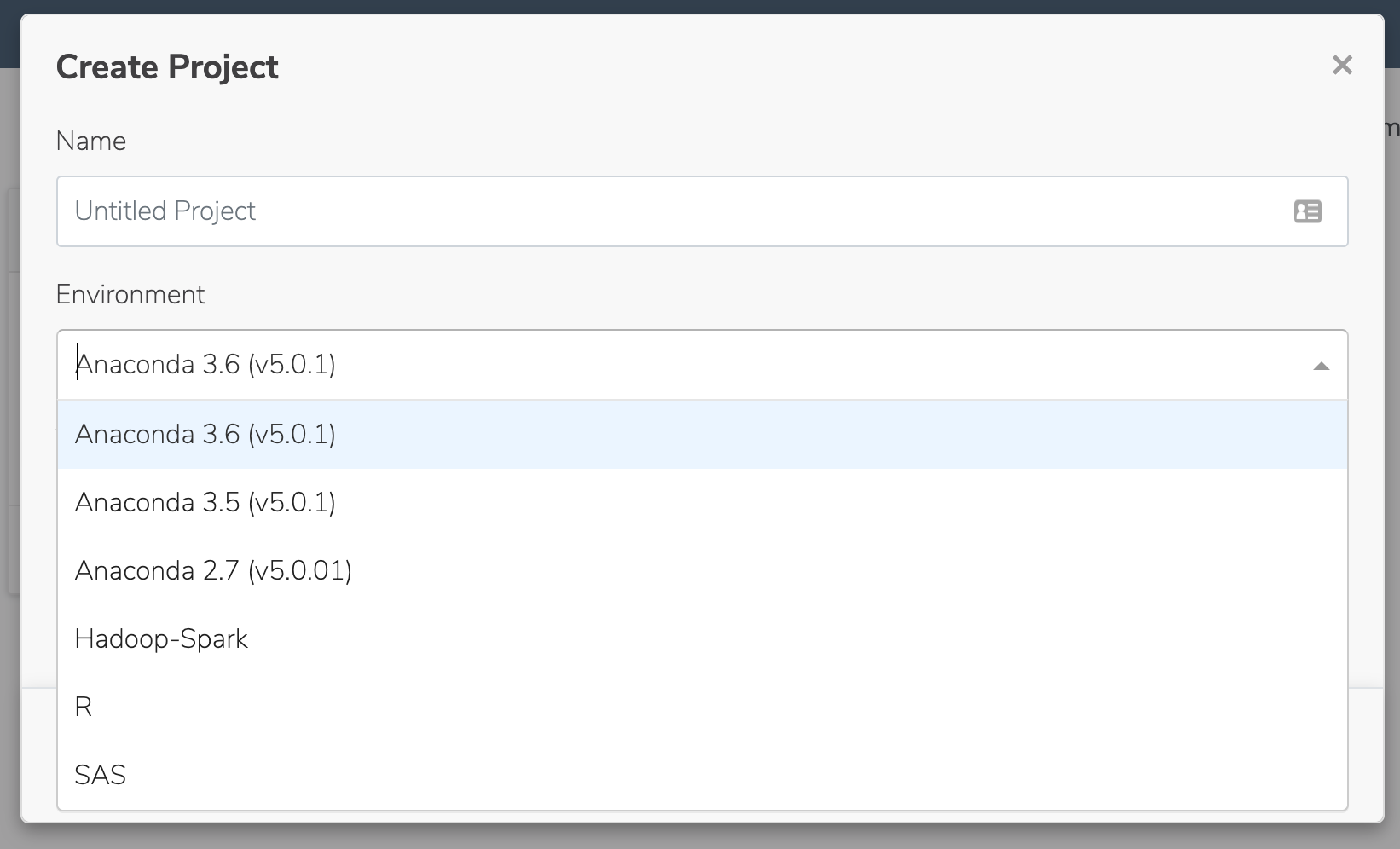
Open the project in a session
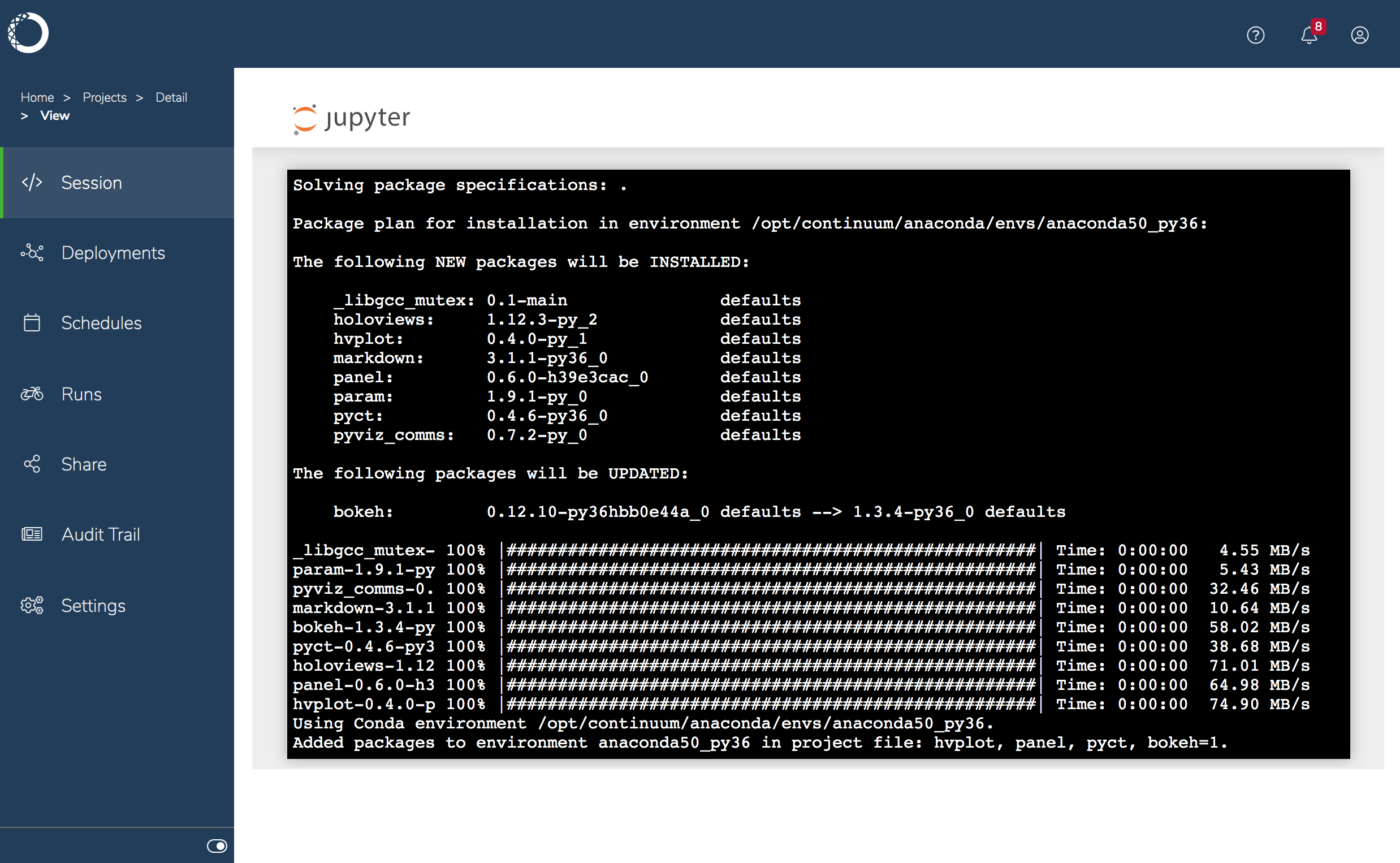
 , select New > Terminal to open a terminal, and run the following command to install packages for
, select New > Terminal to open a terminal, and run the following command to install packages for hvplotandpanel:anaconda-project add-packages hvplot panel
Select New > Python 3 to create a new notebook, rename it
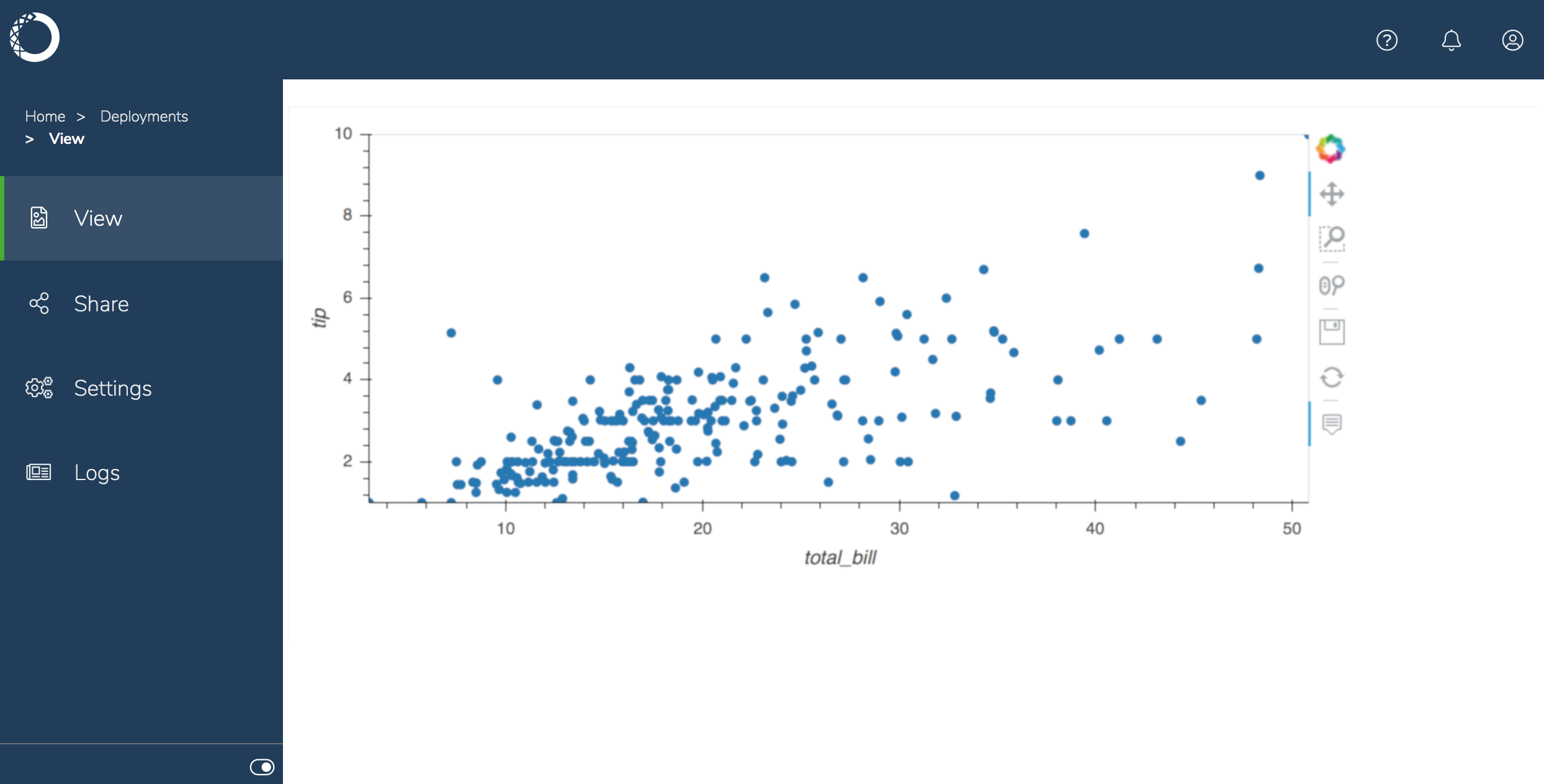
tips.ipynb, and add the following code to create an interactive plot:import pandas as pd import hvplot.pandas import panel panel.extension() df = pd.read_csv('http://bit.ly/tips-csv') p = df.hvplot.scatter(x='total_bill', y='tip', hover_cols=['sex','day','size']) pn.panel(p).servable()
Note
In this example, the data is being read from the Internet. Alternatively, you could download the
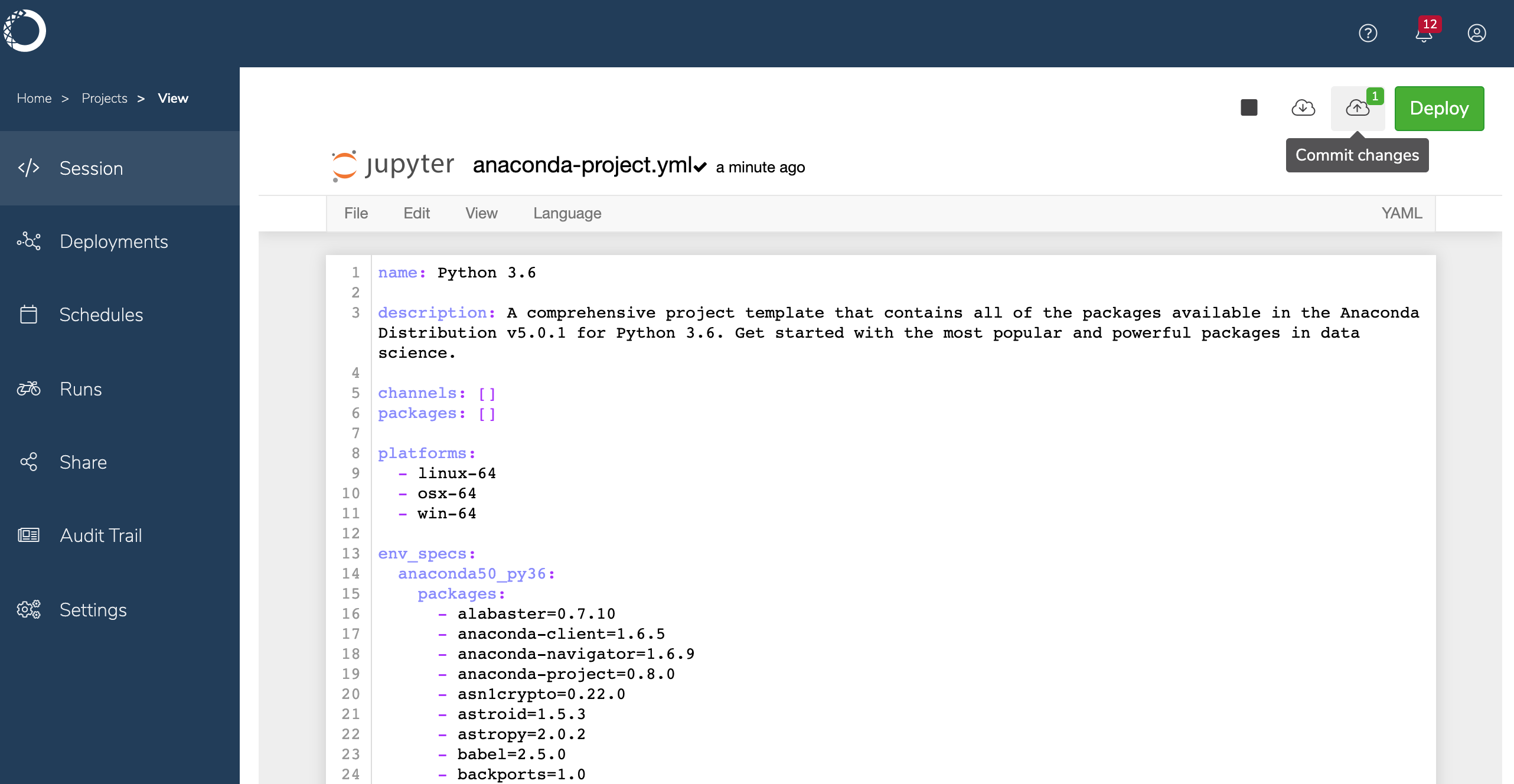
.csvand upload it to the project.Open the project’s
anaconda-project.ymlfile, and add the following lines after thedescription. This is the deployment command that Workbench will use when you deploy the notebookcommands: scatter-plot: unix: panel serve tips.ipynb supports_http_options: True
-
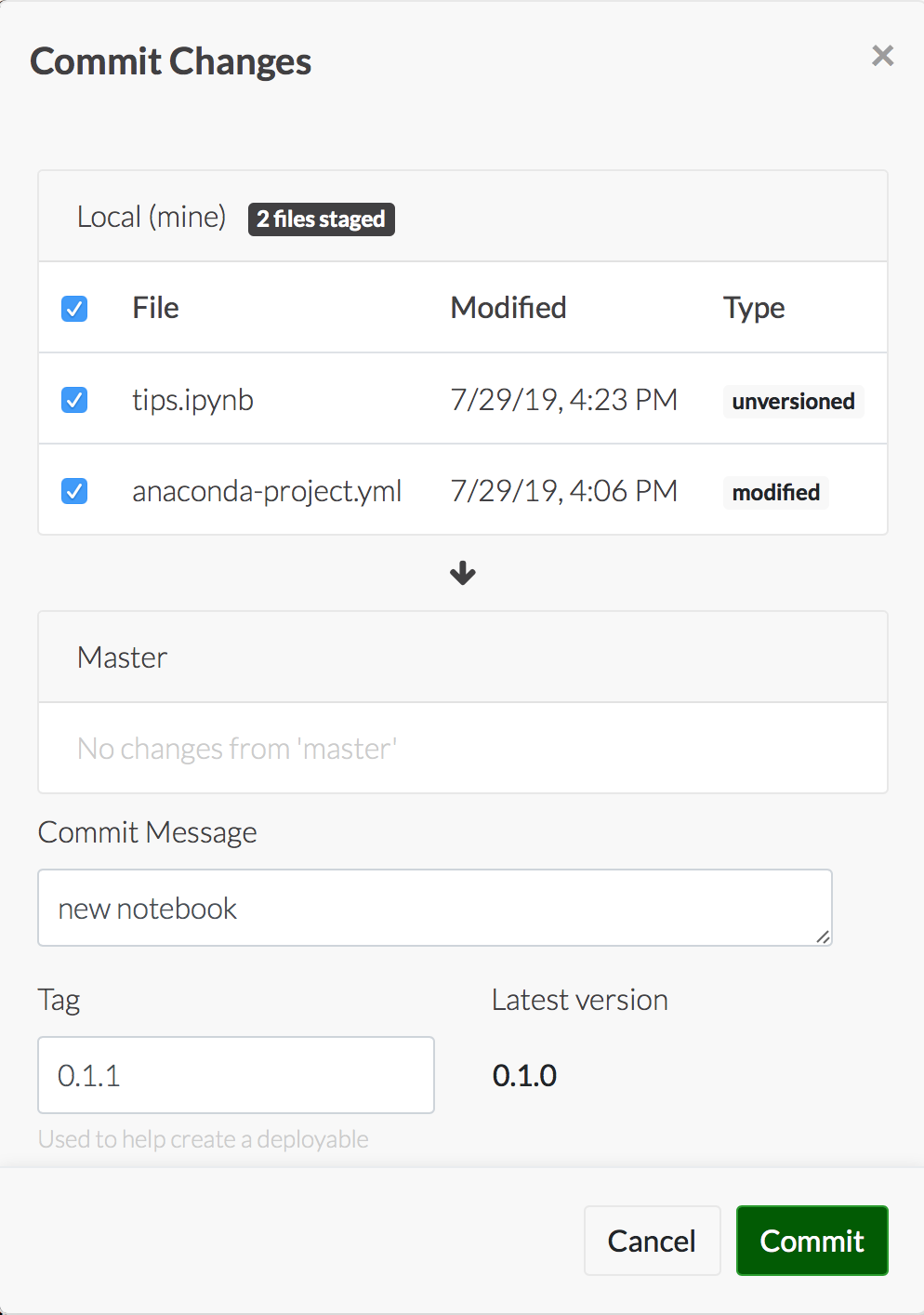
Now you’re ready to deploy the project.
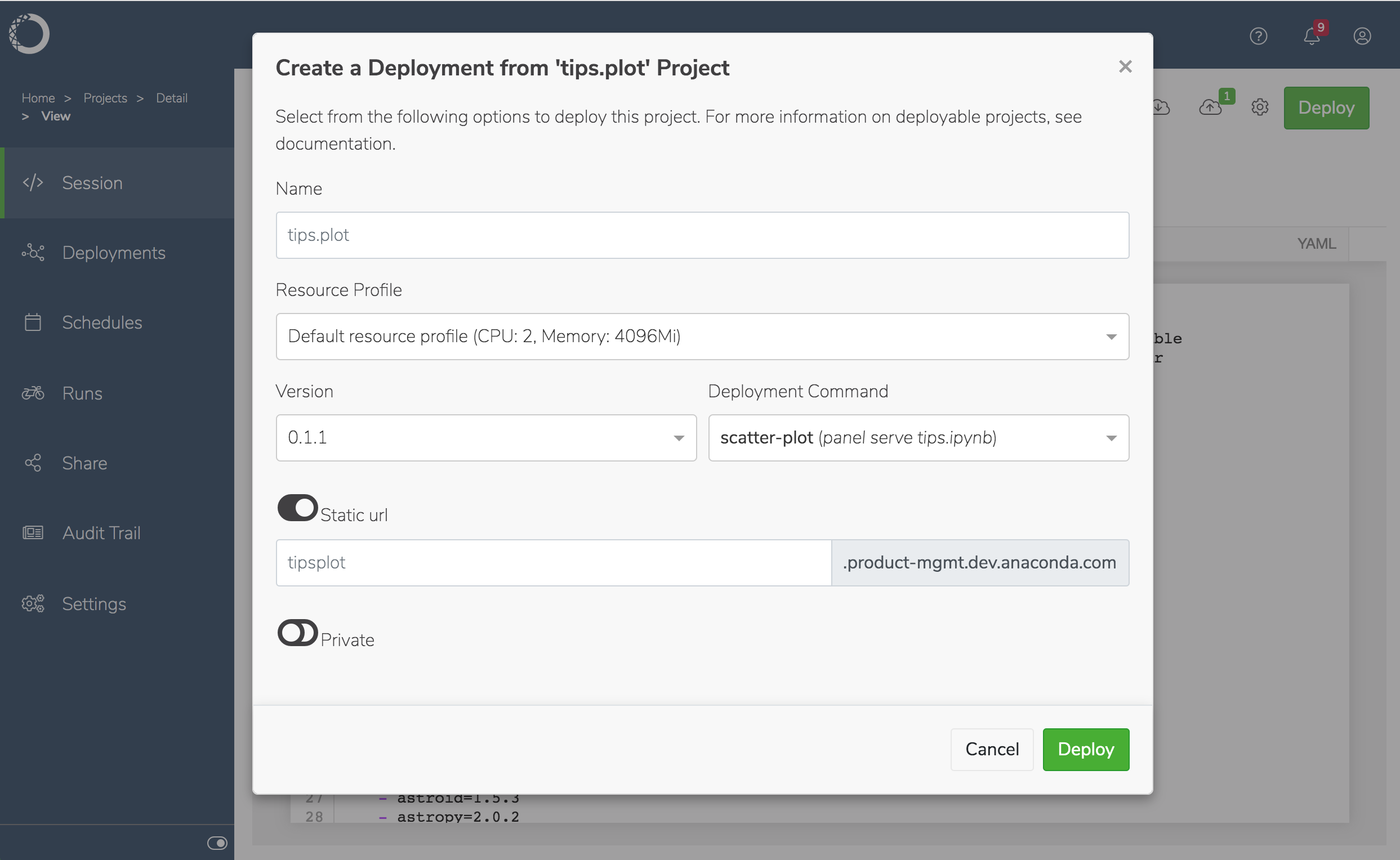
To interact with the notebook—executing its cells without making changes to it—click the deployment’s name.
Tip
To dive deeper into the world of data visualization, follow this HoloViz tutorial.
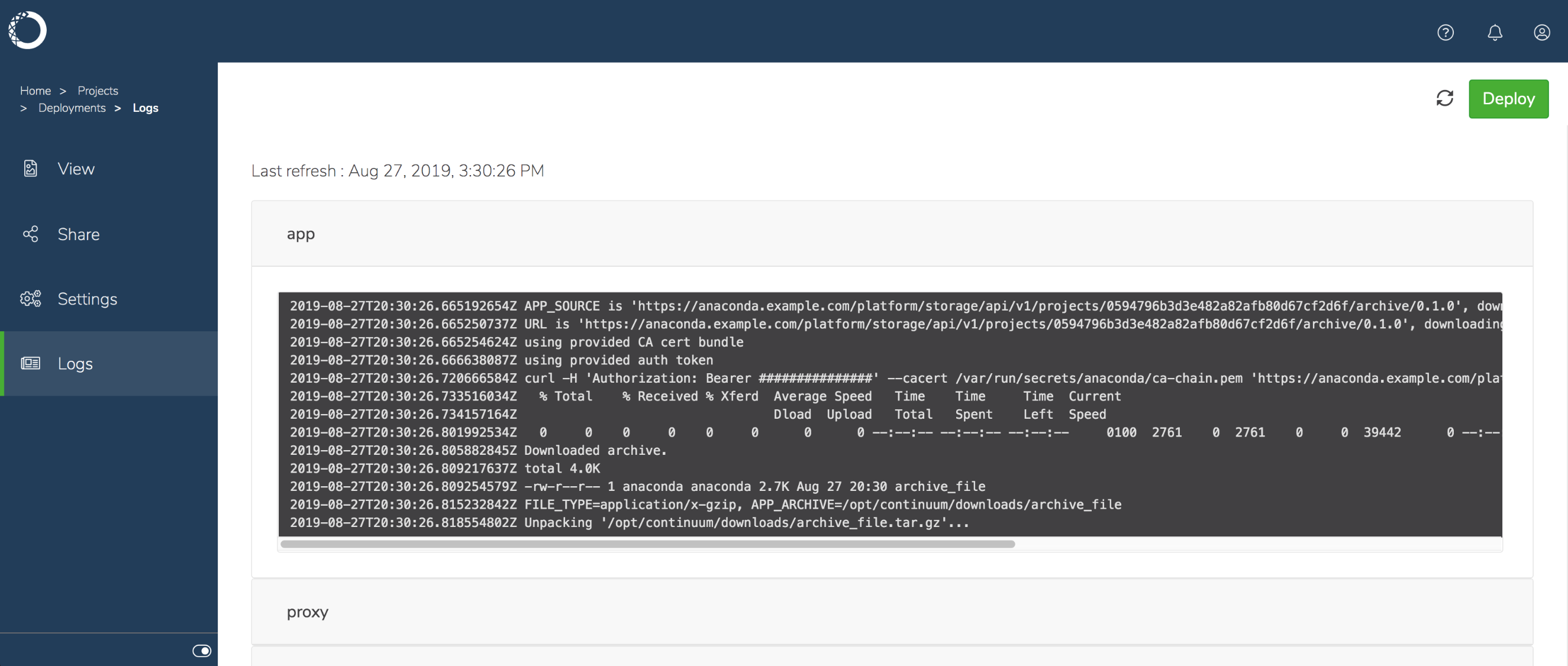
To view and monitor the logs for the deployment while it’s running, click Logs in the left menu. The app section records the initialization steps and any messages printed to standard output by the command used in your project.
You can also share the deployment with others.