Scheduled deployment example#
Here is an example anaconda-project.yml file to demonstrate how to use a scheduled deployment task with scripts and notebooks:
name: Scheduled Job
packages:
- python=3.7
- notebook
channels:
- defaults
platforms:
- linux-64
env_specs:
default: {}
Scripts#
You can run scripts in the correct conda environment by declaring a python executable that’s consistent with the packages specified in the anaconda-project.yml file—in this example, a Python 3.7 Notebook.
The following excerpt of an example anaconda-project.yml file uses an appropriate python executable.
commands:
script_task:
unix: python task.py
In this example, task.py runs the following code, which will print the time and date when the script runs.
from datetime import datetime
print(datetime.now())
Notebooks#
Notebook files cannot be executed using the notebook: command, as that command starts an interactive Jupyter session.
Instead, you can specify a unix: command to execute a Jupyter notebook.
For example, create a simple notebook named task.ipynb, with a single cell:
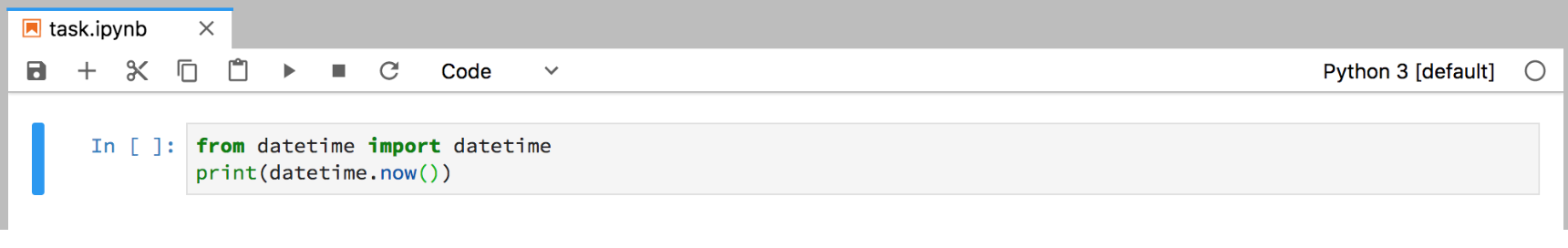
To run the notebook, create another file in the project named run_nb.sh that contains the following:
jupyter nbconvert --ExecutePreprocessor.kernel_name='python3' --to markdown --stdout --execute $1
This run_nb.sh script runs the nbconvert tool against the notebook file, and ensures that:
The Python3 kernel is used
The output is converted to easy-to-ready Markdown
The output is directed to STDOUT rather than a file
Lastly, add the following to the anaconda-project.yml file for the task.ipynb notebook:
commands:
notebook_task:
unix: sh run_nb.sh task.ipynb
After you save and commit your project, you can create a schedule to run it.